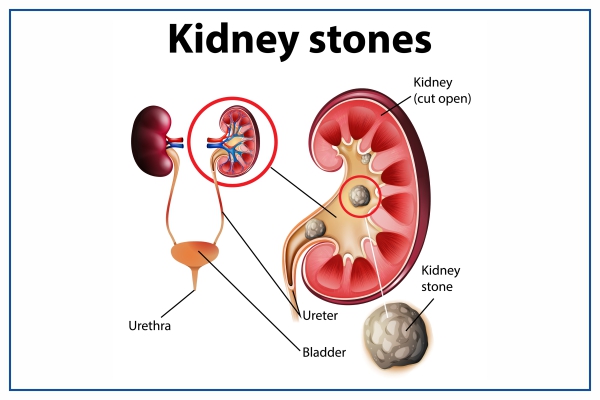
You already know how painful kidney stones can be if you’ve ever had one. In fact, some individuals liken discomfort to childbirth! While kidney stones are a relatively common condition—affecting around 1 in 11 people in the United States—they can still be a bit of a mystery. Here’s what you need to know about kidney stones, and patient experience from risk factors to treatment options.
Risk factors to consider
There are a number of things that can increase your risk of developing kidney stones.
Some of the most common include:
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough fluids can lead to kidney stones because it causes your urine to become more concentrated, which allows minerals and other substances to crystallize and form stones.
- Family history: Your likelihood of developing kidney stones is higher if someone in your family has had them. This may be due to genetics or lifestyle factors that are shared within families.
- Certain medical conditions: Conditions such as Crohn’s disease, renal tubular acidosis, and urinary tract infections can increase your risk of kidney stones.
- Certain medications: Taking drugs such as diuretics (water pills), calcium-based antacids, and some antipsychotic medications can contribute to kidney stone formation.
Treatment Options to consider
Once you have been diagnosed with kidney stones, there are a number of treatment options available. The best course of treatment will depend on the size and location of your stones as well as your overall health.
Treatment options for kidney stones include:
- Drinking plenty of fluids: This is often the first line of treatment for small stones that are not causing too much pain. Drinking lots of fluids helps flush out your system and may help prevent new stones from forming.
- Surgery: Surgery may be necessary if you have large stones that are blocking the flow of urine or causing severe pain. During surgery, the stone is either removed or broken up into smaller pieces so it can pass through your urinary system.
- Medications: Medications such as alpha-blockers and diuretics can help relax the muscles in your urinary tract and allow small stones to pass through more easily. Your doctor may also prescribe pain medication to help relieve any discomfort you’re experiencing.
Conclusion:
Kidney stones are a relatively common condition that can cause severe pain. While there is no surefire way to prevent them, staying hydrated and avoiding certain medications can help reduce your risk.
If you do develop kidney stones, there are a number of treatment options available depending on the size and location of your stones. Talk to your doctor to determine the best course of action for you.